Home
Archives for February 2017
Wednesday, 15 February 2017
program to show prime number in C++.
//Prime number program in dev C++.
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i,num;
cout<<"Enter number:-\n";
cin>>num;
if(num==1)
{
cout<<"1 is not a prime number and smallest prime number is 2";
}
for(i=2;i<num;i++)
{
if(num%i==0)
{
cout<<"number is not prime number";
break;
}
}
if(num==i)
{
cout<<"number is prime number";
}
return 0;
}
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i,num;
cout<<"Enter number:-\n";
cin>>num;
if(num==1)
{
cout<<"1 is not a prime number and smallest prime number is 2";
}
for(i=2;i<num;i++)
{
if(num%i==0)
{
cout<<"number is not prime number";
break;
}
}
if(num==i)
{
cout<<"number is prime number";
}
return 0;
}
Tuesday, 14 February 2017
Swap two number in Turbo C+
//swap two numbers using three variables.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int a,b,c;
clrscr();
cout<<"a=";
cin>>a;
cout<<"b=";
cin>>b;
c=a;//assigning value in c and c is temporary variable.
a=b;
b=c;//assigning value of c in b.
cout<<"after swapping a:"<<a<<"\nb:"<<b;
getch();
}
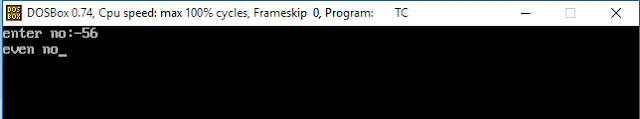
program to check odd or even number in TurboC++
After doing this program you assure that, how to use if and else condition in programs.
//program to check even or odd no:
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int no;
clrscr();
cout<<"enter no:-";
cin>>no;
//checking if no is divisible by two or not.
if(no%2==0)
{
cout<<"\n even no";
}
else
{
cout<<"\n odd no";
}
getch();
}
Tuesday, 7 February 2017
Simple Multiplication table in C++
//Multiplication table in C++ and understand concept of for loop.
#include<iostream.h>
#include<conio.h>
void main()
{
int n,i;
cout<<"\n\t\ This program prints multiplication table:"<<"\n";
cout<<"Enter the value";
cin>>n;
for(i=1;i<=10;i++)
{
cout<<n;
cout<<"*";
cout<<i;
cout<<"=";
cout<<n*i;
cout<<"\n";
}
getch();
}

Monday, 6 February 2017
switch control in C and C++.
Switch condition
switch condition is used to print multiple value as a code or showing different code in same programme.
syntax;
switch(expression)
{
case constant:
code;
break;
case constant:
code;
break;
case constant:
code;
break;
default:
code;
}
different cases are used to show different result.
constant are used to identify each code and it is not compulsory to have constant as a number or character we can take constant as a integer or character as we wish but we did not take constant as a float , like 1.2,1.3 etc.
it is also not compulsory to have constant on a sequence.
we can use switch condition in place of nested-if statement, we can not use nested -if statement in longer programme because it is difficult to read programme.
Saturday, 4 February 2017
Loops in programming languages.
Loops are used to repeat set of codes or a single code. There are three types of loops explained in below;
1)for loop
This loop is very commonly used and syntax is very easy.
syntax;
for(var initialization; var condition; increament of variable)
for example;
for(i=0;i<=10;i++)
{
cout<<"";
or
printf("");
}
2)while loop
while loop is very simple and syntax is ;
while(condition)
{
}
while(x<=10)
{
}
3)do-while loop
syntax;
do{
printf();
}
while();
1)for loop
This loop is very commonly used and syntax is very easy.
syntax;
for(var initialization; var condition; increament of variable)
for example;
for(i=0;i<=10;i++)
{
cout<<"";
or
printf("");
}
2)while loop
while loop is very simple and syntax is ;
while(condition)
{
}
while(x<=10)
{
}
3)do-while loop
syntax;
do{
printf();
}
while();
Subscribe to:
Comments (Atom)



